CT Reconstruction #
Analytical CT reconstruction #
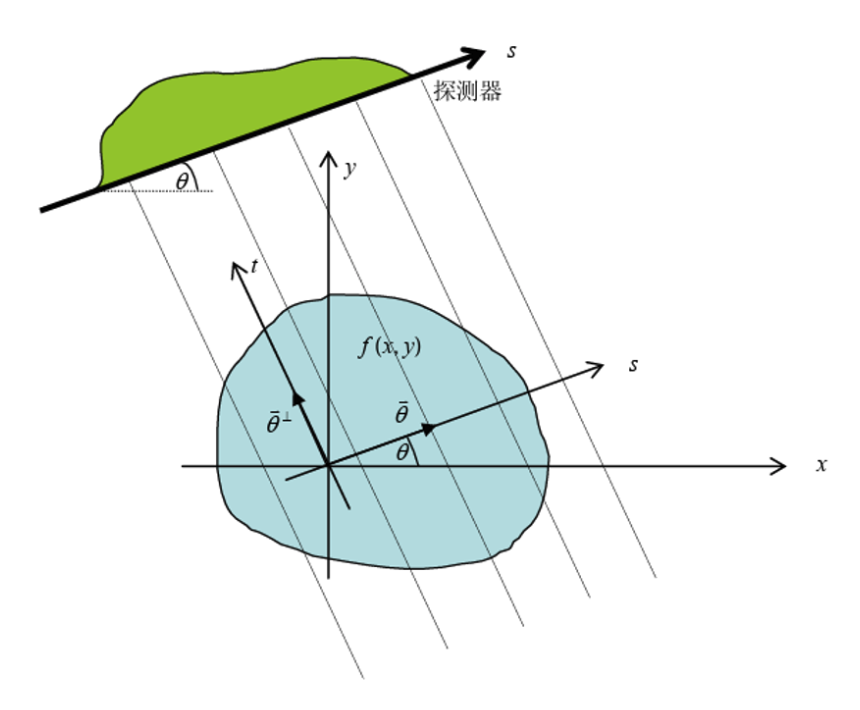
Radon Transform
数学形式化描述
$$ p(s,\theta)=\int^\infty_{-\infty}\int^\infty_{-\infty}f(x,y)\delta(xcos\theta+ysin\theta-s)dxdy $$
- $s,\theta$确定时,相当于仅在直线$xcos\theta+ysin\theta-s=$上作积分
代码实现
from skimage.transform import warp
theta = np.arange(180)
# pad
padded_image = np.pad(image, pad_width, mode='constant',
constant_values=0)
center = padded_image.shape[0] // 2
# 旋转+投影
radon_image = np.zeros((padded_image.shape[0], len(theta)),
dtype=image.dtype)
for i, angle in enumerate(np.deg2rad(theta)):
cos_a, sin_a = np.cos(angle), np.sin(angle)
R = np.array([[cos_a, sin_a, -center * (cos_a + sin_a - 1)],
[-sin_a, cos_a, -center * (cos_a - sin_a - 1)],
[0, 0, 1]])
rotated = warp(padded_image, R, clip=False)
radon_image[:, i] = rotated.sum(0)
Sinogram
正弦图的每一个$\theta$都对应一组s轴上的投影

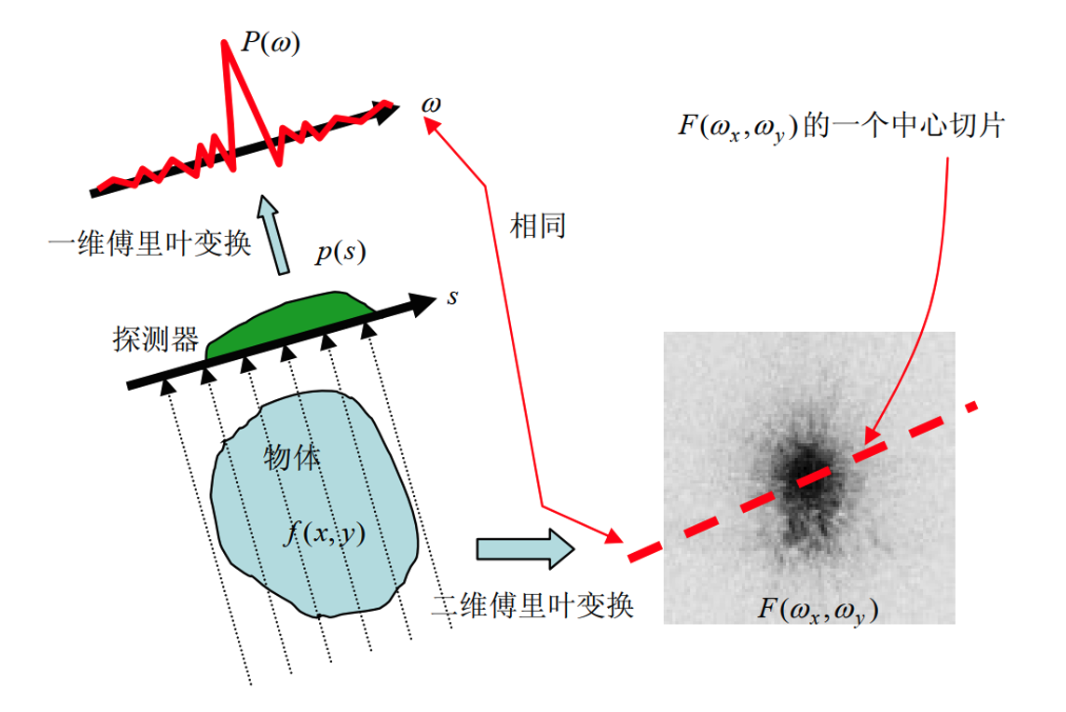
中心切片定理
二维图像的中心切片定理指出:二维函数 f(x, y) 的投影 p(s) 的傅里叶变换 P(ω) 等于函数 f(x, y) 的傅里叶变换 F(ωx,ωy) 沿与探测器平行的方向过原点的片段。
FilteredBackProjection (FBP)
证明:

数学形式化描述
$$f(x,y)=\int^\pi_0q(s,\theta)|_{s=x\cos\theta+y\sin\theta}d\theta$$
代码实现
reconstructed = np.zeros((output_size, output_size),dtype=dtype)
radius = output_size // 2
xpr, ypr = np.mgrid[:output_size, :output_size] - radius
for col, angle in zip(radon_filtered.T, np.deg2rad(theta)):
t = ypr * np.cos(angle) - xpr * np.sin(angle)
reconstructed += interpolant(t)
reconstructed = reconstructed* np.pi / (2 * angles_count)
MRI Reconstruction #
Image Enhancement & Restoration #
Image Quality Assessment #
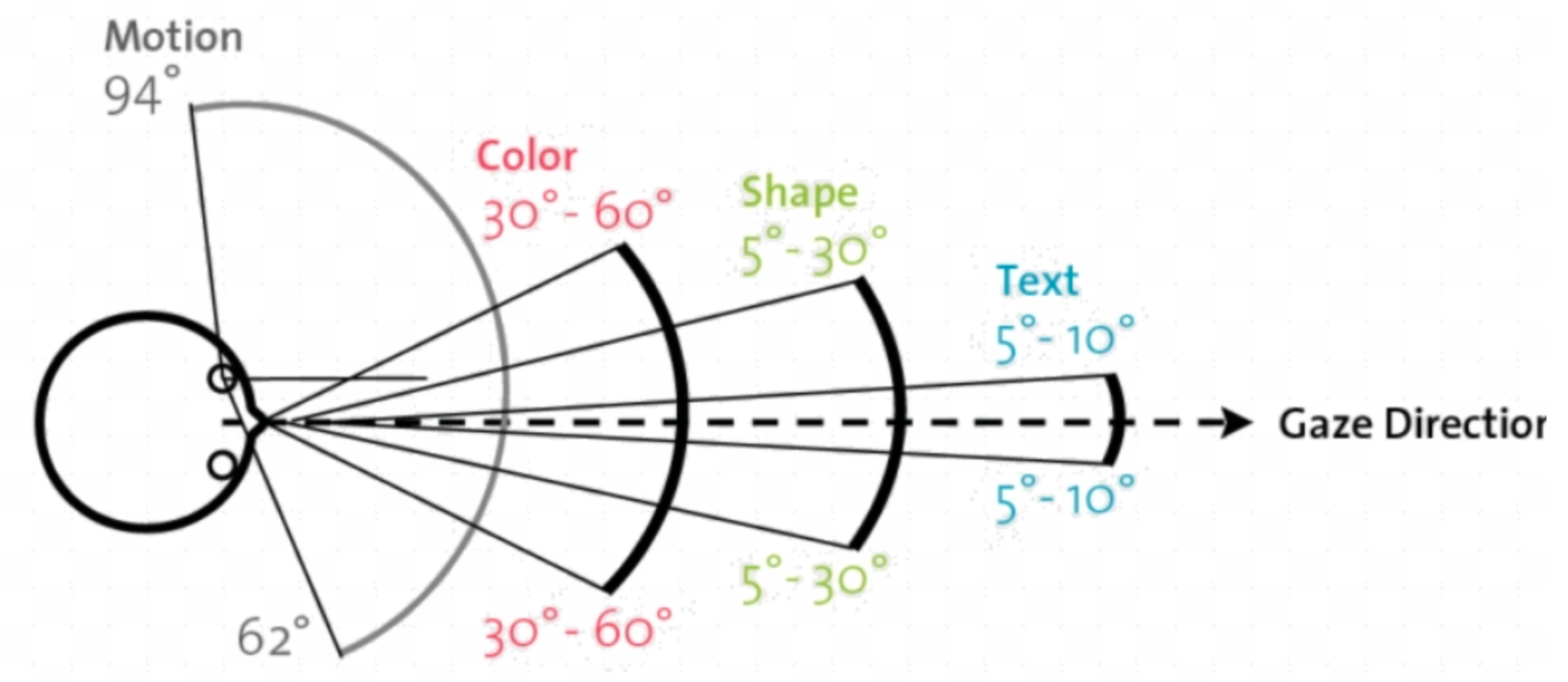
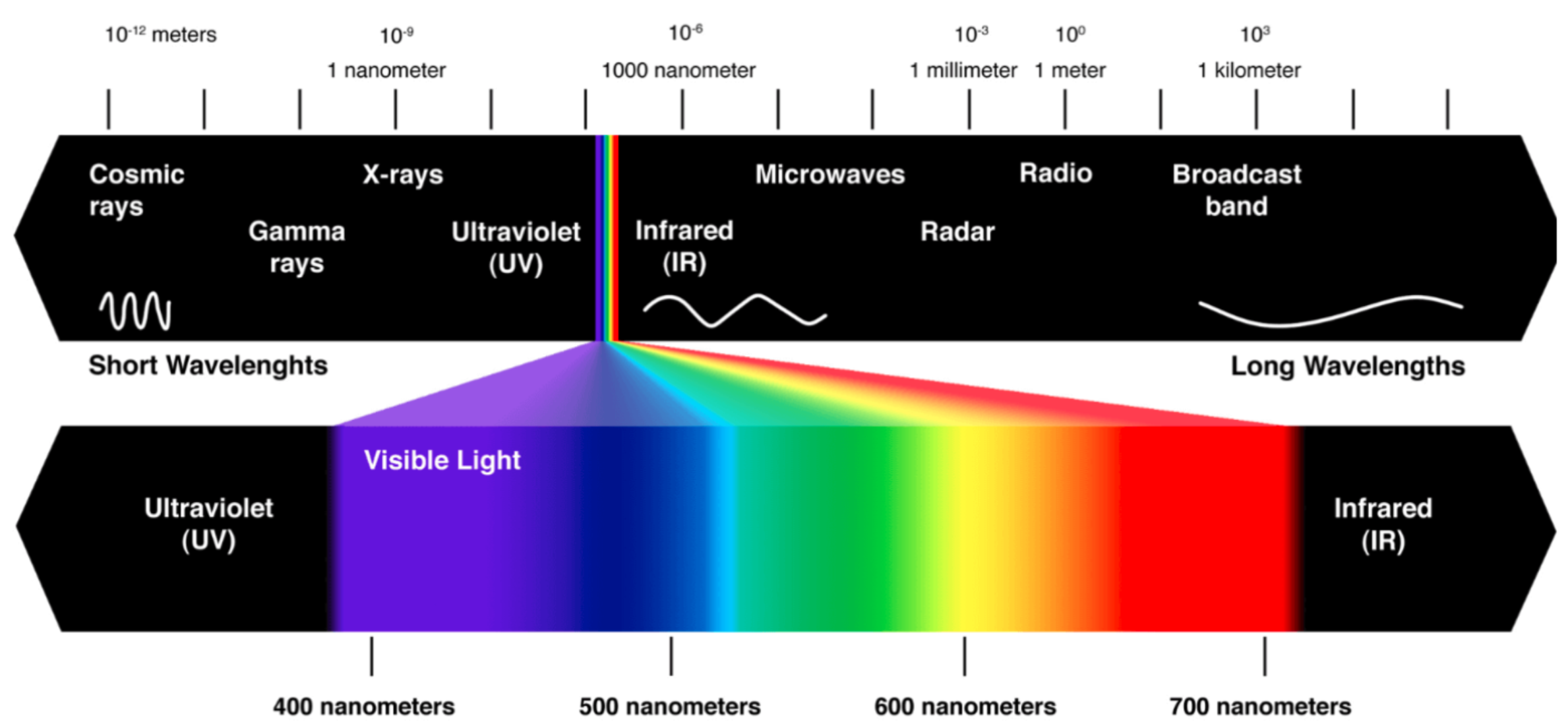
Human visual system (HVS)
| 视敏度 | visual acuity | 20/20 is ~1 arc minExtreme acuity = 0.4 arc min =1/150 of a degree |

|
|---|---|---|---|
| 视野 | field of view | ~190° monocular, ~120° binocular, ~135° vertical |
|
| 空间分辨率 | spatial resolution | ~576 megapixels | |
| 时间分辨率 | temporal resolution | ~60 Hz | |
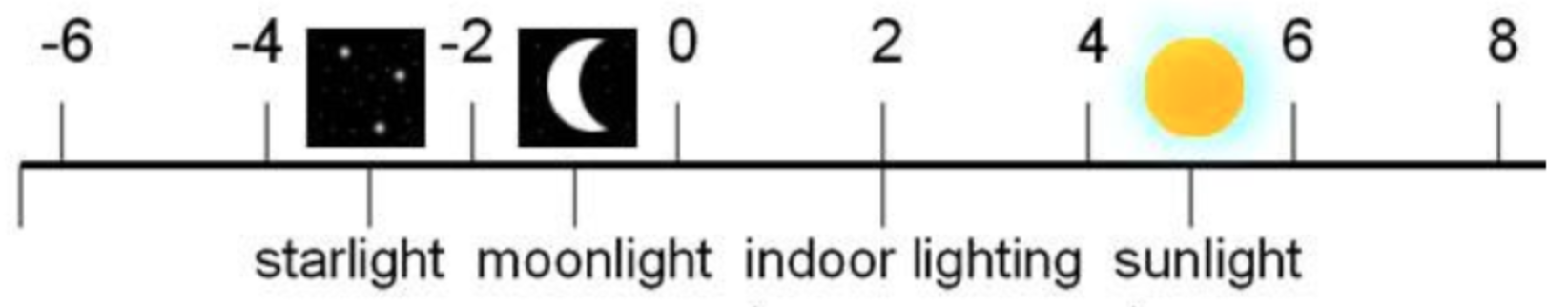
| 动态范围 | dynamic range |
|
|
| 颜色 | color |
|
|
| 深度 | depth cues in 3D displays | ||
| 聚焦范围 | accommodation range | ~8cm to ∞, degrades with age |
Image Quality Metric
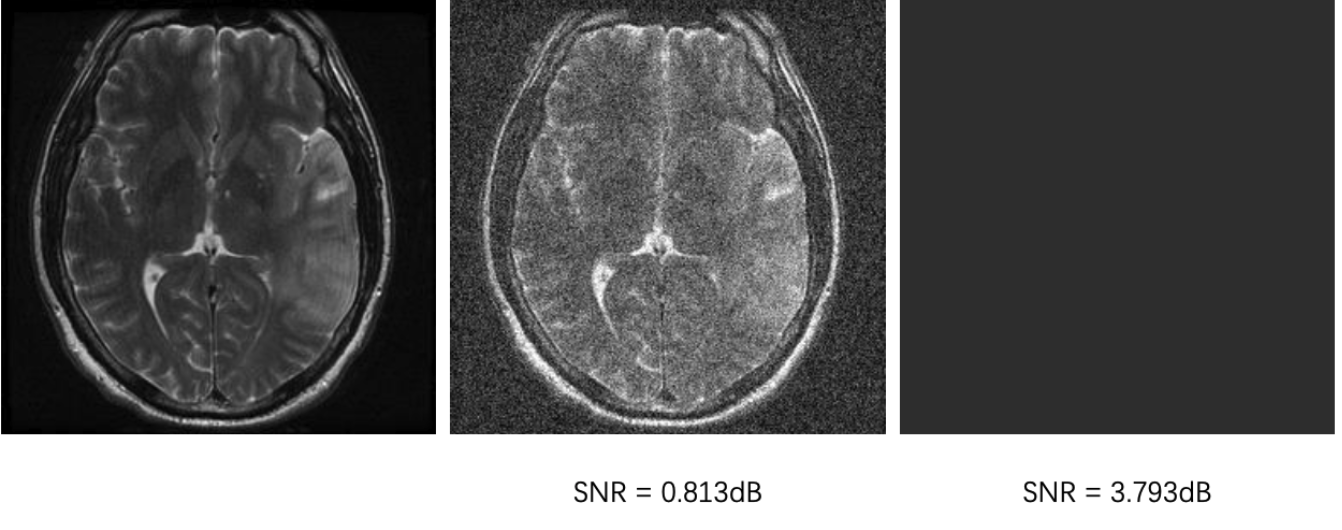
| Signal-to-Nosie Ratio (SNR) | Is SNR a good metric? Nope! | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Structural similarity index measure (SSIM) | $$ssim(x, y)={l(x, y)}^{\alpha} {c(x, y)}^{\beta} {s(x, y)}^{\gamma}$$ | |
| $$luminance\ l(x, y)=\frac{2\mu_x\mu_y+c_1}{\mu_x^2+\mu_y^2+c_1}$$$$contrast\ c(x, y)=\frac{2\sigma_x\sigma_y+c_2}{\sigma_x^2+\sigma_y^2+c_2}$$$$structure\ s(x, y)=\frac{2\sigma_{xy}+c_3}{\sigma_x\sigma_y+c_3}$$ | ||
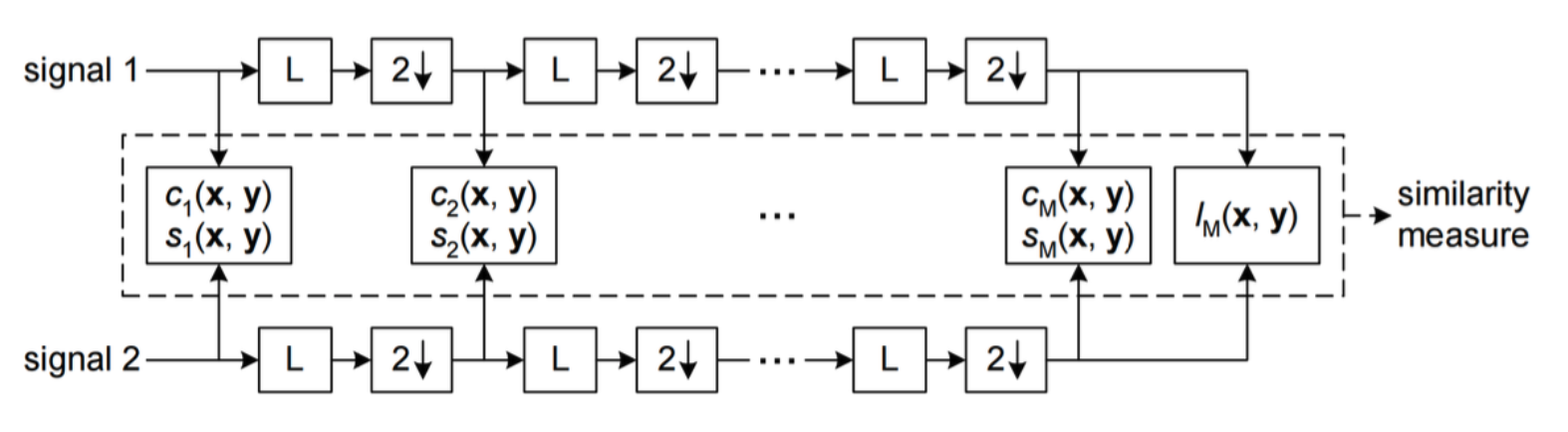
| Multi-scale SSIM |
|
No-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA)
| Blind/Reference-less Image Spatial Quality Evaluator (BRISQUE) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Naturalness Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE) | ||
| Perception-based Image Quality Evaluator (PIQE) |
Image Enhancement #
Global (or spatially uniform) operators
| Reinhard | $$I_{out}=\frac{I_{in}}{I_{in} + 1}$$ | |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma compression | $$I_{out}=AI_{in}^\gamma$$ | |
| Look-up table (LUT) | ||
| Histogram equalization | 寻找$$s=T(r)$$使得$$f(s)=f(r)\frac{dr}{ds}=\frac{1}{L-1}$$,易得$$\frac{ds}{dr}=f(r)(L-1)$$,积分可得$$s=\int_0^r{f(r)(L-1)dr}$$ |
Local (or spatially varying) operators
| Unsharp masking | $$I_{out}=I_{in}+\lambda Z$$$$Z=HF(I_{in})=I_{in}-LF(I_{in})$$ | 增强低频/高频分量 |
|---|---|---|
| Guassian/Bilateral/… Filtering |
Gradient domain tone mapping
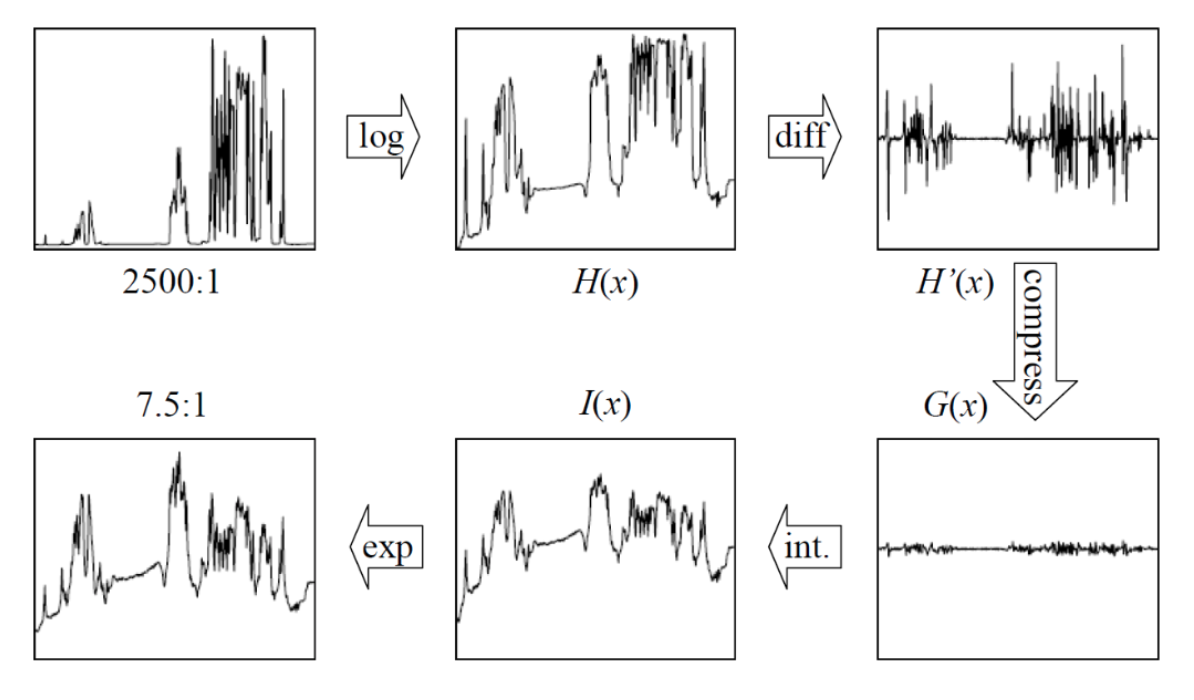
- Multiscale tone-mapping
Image Restoration #
Imaging model
| Noise | Expression | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Blur(Multiplicative) | $$Y=AX$$ | Deblur |
| Downsample | $$Y=\downarrow_r X$$ | Superresolution |
| Mask | $$Y=X(1-M)+ZM$$ | Inpainting |
| Noise (Addictive) | $$Y=AX+N$$ | Denoise |
Direct method: function approximation
| Mean filter | Assumptions: 噪声和信号独立,噪声相互独立$$E(\overline{N}^2)=\frac{1}{n}\sigma^2$$ $$ SNR_{avg} = nSNR_{orig}$$ | |
|---|---|---|
| Gaussian filter | $$f(p)=\frac{1}{\Sigma_{p\in\Omega} f(p-s)}\Sigma_{p\in\Omega} f(p-s)I_p$$ | 距离越近,权重越大 |
| Edge-preserving filter | 三大保边滤波,防止边缘因滤波而模糊 | |
| Bilateral filter (BF) | $$f(p)=\frac{1}{\Sigma_{p\in\Omega} f(p-s)g(I_p-I_s)}\Sigma_{p\in\Omega} f(p-s)g(I_p-I_s)I_p$$ | 距离越近,像素值越接近,权重越大 |
| Guided filter (GF) | $$O_i=\overline{a_k}G_i+\overline{b_k}$$其中$$a_k=\frac{Cov_{W_k}(G,I)}{Var_{W_k}(G)+\epsilon}$$, $$b_k=E_{W_k}(I)-a_kE_{W_k}(G)$$ | 物理意义等等再写 |
| Weighted least squares filter(WLSF) | ||
| Nonlocal Means | 在全局范围内计算权重 | |
| Block-matching and 3D filter (BM3D) | Block-matching: 寻找相似的图像块3D Filter: 在堆叠的图像块上进行3D滤波Aggregation: 3D->2D |
Implicit method: A probabilistic framework for denoising
由$$Y=AX+$$可得$$Y-AX=N$$,进一步有$$f(Y|X)=f(N)$$
假定噪声服从高斯/拉普拉斯/泊松分布,则获得了$$f(Y|X)$$的含参数表达式
使用极大似然估计,可以得到参数的估计值
$${argmax}{\sigma, X} P(Y|X)={argmin}{\sigma, X} -logP(Y|X)$$
假定噪声服从Gaussian分布,则有$$X=argmin_{X}|Y-AX|^2/2\sigma^2$$
假定噪声服从Laplacian分布,则有$$X=argmin_{X}|Y-AX|/2\sigma$$
Bayesian/optimization approach
$$max_X P(X|Y)=P(Y|X)P(X)/P(Y)$$
$$min_X L(X)=|Y-AX|^2/2\sigma^2+\lambda R(X)$$
R(X)是X的正则项/反转分布,取决于对X的先验
Image prior: Sparsity presentation
Dictionary learning: to find D
- Sparse coding
$$min_{\alpha} |\alpha|_0\ subject\ to\ x=D\alpha$$
- Denoising (given D)
$$min_\alpha |\alpha|_0{\ subject \ to}|x-D\alpha|_2<\varepsilon$$
Which dictionary to use?
- Choose D from a known set of transforms
Eg. Fourier Transform/Cosine Transform/Steerable wavelet/Curvelet/Contourlets/Bandlets/Shearlets
- Learn D from a set of examples
Such learning should sparsify the representation as much as possible.
Image Segmentation #
Distance
Connection
Polar
中心扩散/梯度
根据物体的形状/…特点寻找合适的表达
Threshold: m(x,y)=F(I(x,y))>t
Water
Region growing
cluster